udmi
UDMI / Docs / Specs / Sequences / Config
Config & State Sequence
- The
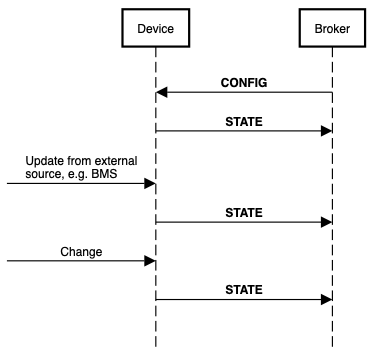
stateandconfigmessages work together to represent a transactional state between the cloud and device. - When any
configis received, astateupdate should be generated with a corresponding last_update. - The state message should be sent within 5 seconds
- If additional processing is required, then the
updatingflag should be settrue. updatingshould be returned tofalse(or absent) once the device is done updating.
- If additional processing is required, then the
- The device can asynchronously update
stateif some other condition changes independent ofconfigmessage, including when:- There is an update from an external source, e.g. a BMS or local controller
- There is an update from internal logic
- Other sequences such as writeback may have specific behaviors relating to state messages
- A device should of continuously operating when receiving an erroneous config message. The
Generated using <https://sequencediagram.org>
participant Device
participant Broker
participantspacing 5
Broker->Device: **CONFIG**
Device->Broker: **STATE**
[->Device:Update from external\nsource, e.g. BMS
Device->Broker: **STATE**
[->Device:Change
Device->Broker: **STATE**
Config Message
timestamp: Server-side timestamp of when the config was generated.system: Subsystem for system-level information.- …: Other subsystems as defined in the standard (e.g. pointset or gateway).
State Message
system:last_config: Server-side timestamp from the last processedconfig.updating: Boolean indicating if the system is still processing the lastconfigupdate.
Erroneous Config Handling
A device should be capable of interpreting erroneous messages without disrupting operation. There are three types of errors which may be encountered when interpreting config messages:
- Hard-errors
- Soft-errors
- Non-errors
This behavior is tested by the config sequencer tests.
Hard-errors
Hard errors are ones such that the sanity of the entire config block is held in question, and considered “invalid” at a core level. This can happen when:
- Only in response to config update message received
- Payload does not pass JSON parsing
- Missing “required” parameters (e.g. top-level version field)
- NOT by unrecognized extra JSON fields
When this happens, the device should:
- Keep the previous config (and use it) as a “steady state”
- The state system.last_update time should not be updated
- Appropriate error message included in system.statuses.config
- All other status blocks (pointset, etc…) should remain unaffected
Soft-errors
Are things that can be safely relegated to a specific sub-block (e.g. pointset) without other areas being affected. This can happen when:
- Invalid operations are indicated (e.g. writeback to non-writable point)
- There is no blanket conditions for all subblocks (just depends)
- Possibly independent of config (internal to device changes)
- Can happen to multiple subblocks independently
When this happens, the device should:
- Update system.last_config with last config.timestamp (config change)
- Indicate relevant error (most significant) in system.statuses.{subblock}
- Indicate more error detail (if any) in irrelevant state sunblock
- Include additional error information in log messages (if appropriate)
- Continue operating as best possible given the specified (invalid) config
Non-Errors
There are some things that are specifically non-errors, and essentially meant to enable/help with backwards compatibility. This can happen when:
- There is an extra unknown field in a config json message.
When this happens, the device should:
- Silently ignore the extra field(s) as if there was nothing wrong.
- Generally can be implemented by setting some JSON parsers to “ignore unrecognized fields”